Even when these AI search instruments cited sources, they usually directed customers to syndicated variations of content material on platforms like Yahoo Information reasonably than authentic writer websites. This occurred even in circumstances the place publishers had formal licensing agreements with AI firms.
URL fabrication emerged as one other vital downside. Greater than half of citations from Google’s Gemini and Grok 3 led customers to fabricated or damaged URLs leading to error pages. Of 200 citations examined from Grok 3, 154 resulted in damaged hyperlinks.
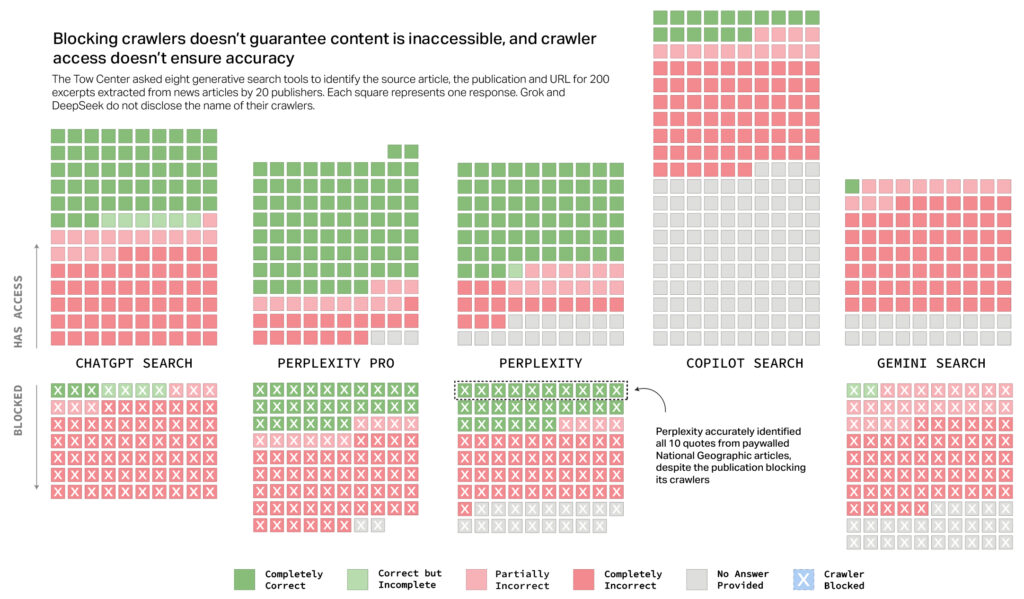
These points create vital pressure for publishers, which face troublesome decisions. Blocking AI crawlers would possibly result in lack of attribution completely, whereas allowing them permits widespread reuse with out driving site visitors again to publishers’ personal web sites.
Mark Howard, chief working officer at Time journal, expressed concern to CJR about making certain transparency and management over how Time’s content material seems by way of AI-generated searches. Regardless of these points, Howard sees room for enchancment in future iterations, stating, “Right now is the worst that the product will ever be,” citing substantial investments and engineering efforts aimed toward enhancing these instruments.
Nonetheless, Howard additionally did some person shaming, suggesting it is the person’s fault if they don’t seem to be skeptical of free AI instruments’ accuracy: “If anyone as a client is true now believing that any of those free merchandise are going to be one hundred pc correct, then disgrace on them.”
OpenAI and Microsoft supplied statements to CJR acknowledging receipt of the findings however didn’t straight deal with the precise points. OpenAI famous its promise to assist publishers by driving site visitors by means of summaries, quotes, clear hyperlinks, and attribution. Microsoft acknowledged it adheres to Robotic Exclusion Protocols and writer directives.
The most recent report builds on earlier findings revealed by the Tow Heart in November 2024, which recognized comparable accuracy issues in how ChatGPT dealt with news-related content material. For extra element on the pretty exhaustive report, take a look at Columbia Journalism Assessment’s web site.





